In the dynamic realm of artificial intelligence (AI) design, ethical considerations serve as guiding stars illuminating our path forward. As we traverse the intricate landscapes of innovation, it’s imperative to pause and reflect on the profound implications of our creations. Join me on a journey as we delve into the moral dimensions of AI design, exploring poignant examples that underscore the ethical crossroads we encounter.
Let’s start by taking a look at two important examples of recent AI integration in the real world!
The Good: Voices From the Front

Step into the hallowed halls of the National WWII Museum in New Orleans, where history converges with cutting-edge technology in the groundbreaking project “Voices From the Front.” This innovative initiative harnesses the power of AI to preserve the invaluable narratives of World War II veterans, ensuring their stories transcend time for future generations.
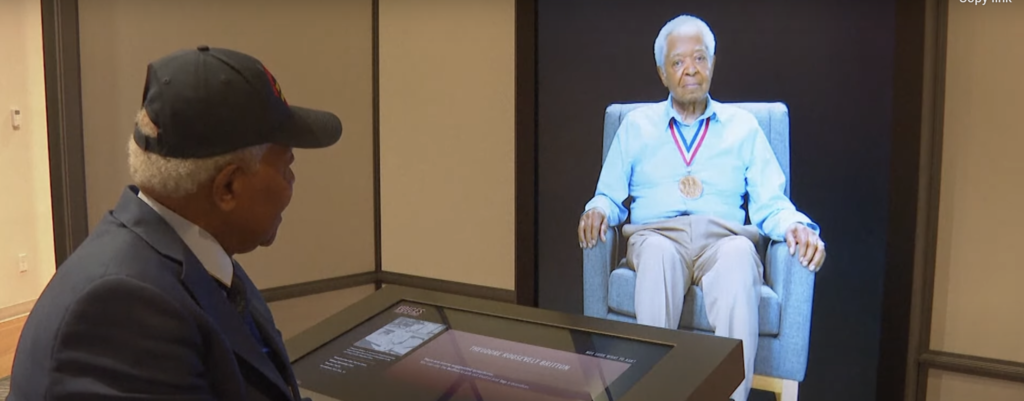

Through life-sized projections and advanced algorithms, visitors engage in virtual conversations with veterans, experiencing firsthand the profound impact of their experiences. From tales of valor on distant battlefields to poignant reflections on sacrifice and camaraderie, “Voices From the Front” stands as a testament to the enduring legacy of those who served. As we marvel at the convergence of history and innovation, we’re reminded of the ethical imperative to honor and preserve the voices of the past.
The Bad: Casting Shadows on Creativity

In the realm of creative expression, the BBC’s decision to replace actress Sara Poyzer with AI in an upcoming project casts a shadow on the intersection of technology and artistry. The use of AI-generated voices in place of human actors sparks debates surrounding the ethical implications and the preservation of human creativity.
While the BBC cites noble intentions in recreating the voice of a contributor unable to speak, concerns arise regarding the broader implications for the creative industries. As voices from the industry express dismay and apprehension, we’re prompted to confront the ethical quandaries posed by the growing influence of AI in media production. The incident serves as a poignant reminder of the delicate balance between technological advancement and the preservation of human ingenuity.
What Can We Do? (as designers)

As we navigate the complex terrain of AI design, ethical considerations emerge as beacons guiding our decisions. Designers must tread carefully, mindful of the profound impact their creations wield on society.
Transparency: Designers must prioritize transparency in AI systems, ensuring that users understand how their data is collected, processed, and utilized. Transparent AI fosters trust and empowers users to make informed decisions about their interactions with technology.
Accountability: Ethical AI design necessitates accountability mechanisms that hold designers and developers responsible for the consequences of their creations. Establishing clear lines of accountability ensures that ethical lapses are identified, addressed, and rectified promptly.
Fairness and Bias Mitigation: AI systems have the potential to perpetuate or exacerbate societal biases, leading to unfair outcomes for marginalized groups. Designers must proactively mitigate bias by employing diverse datasets, conducting bias assessments, and implementing algorithms that prioritize fairness and equity.
Privacy Preservation: Respecting user privacy is paramount in AI design, requiring stringent safeguards to protect sensitive personal information from unauthorized access or misuse. Designers must prioritize data minimization, encryption, and user-centric privacy controls to uphold individual privacy rights.
Human-Centric Design: Ethical AI design centers on human well-being, prioritizing solutions that enhance human dignity, autonomy, and agency. Designers should adopt a human-centric approach that considers the social, cultural, and ethical implications of AI systems on individuals and communities.
Inclusivity and Accessibility: AI systems should be designed with inclusivity and accessibility in mind, ensuring that they are usable and beneficial for all individuals, regardless of age, ability, or background. Designers must address barriers to access and actively involve diverse stakeholders in the design process to create solutions that serve the needs of all users.
Safety and Security: Ethical AI design encompasses robust measures to ensure the safety and security of AI systems, guarding against potential vulnerabilities, malicious attacks, and unintended consequences. Designers should prioritize system resilience, data integrity, and cybersecurity protocols to mitigate risks and protect users from harm.
Long-Term Impact: Designers must consider the long-term societal impact of AI systems, anticipating potential downstream effects on employment, education, healthcare, and other facets of daily life. Ethical foresight enables designers to proactively address emerging challenges and steer AI innovation towards positive social outcomes.
In the ever-evolving landscape of AI design, the ethical compass serves as our North Star, guiding us towards a future where innovation is synonymous with integrity. By embracing ethical principles and confronting moral dilemmas head-on, we pave the way for a world where AI uplifts humanity while preserving the essence of our shared humanity. As stewards of innovation, let us embark on this ethical journey with courage, compassion, and unwavering commitment to the greater good.
 Navigating the Ethical Crossroads: Designing AI with a Moral Compass
Navigating the Ethical Crossroads: Designing AI with a Moral Compass